

A system is an organised collection of resources
and processes that work together to
achieve a purpose and ultimately fulfil a
need.
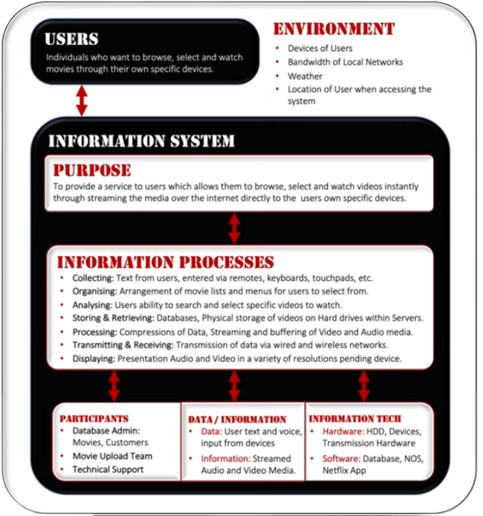
An information system needs participants, data or information, and information technology to carry out a number of information processes. It handles a variety of information processing functions, including data gathering, organisation, analysis, storing and retrieval, processing, transmission and reception, and display.
Netflix is an on-demand streaming service that
allows users to search for and watch videos on
almost any of their own devices.
Once the user selects what they wish to see, the
video and audio data are delivered to the user's
selected device very quickly.
In the field of on-demand streaming services,
Netflix is a pioneer. promoting the format so
that more platforms will use it.
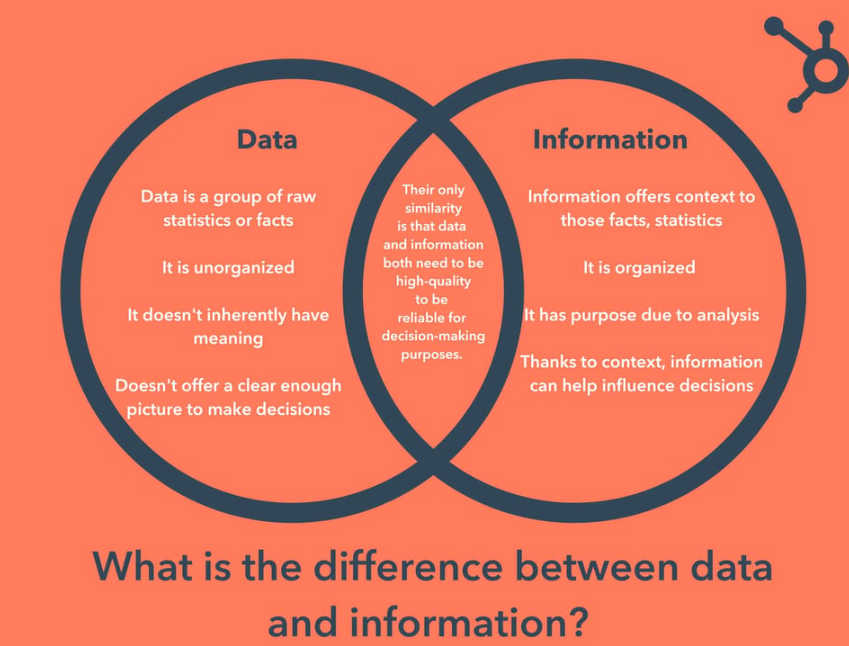
Data is the raw, unprocessed resources that are collected for further use.
This raw material could be in the form of images, audio, video, text or numbers and it is inputted into an input device.
Information is referred to as a collection of facts that have been arranged in some way such that, when taken as a whole, they can be comprehended and given meaning.
When referring to IT and systems,
information means the output displayed
by an information system, as a result
knowledge is acquired when
information is received.
Data and information may sound very similar, however, they are not the same. Data refers to the raw and unprocessed materials that need to be processed. Once the data is processed into a useful manner, it is referred to as information.
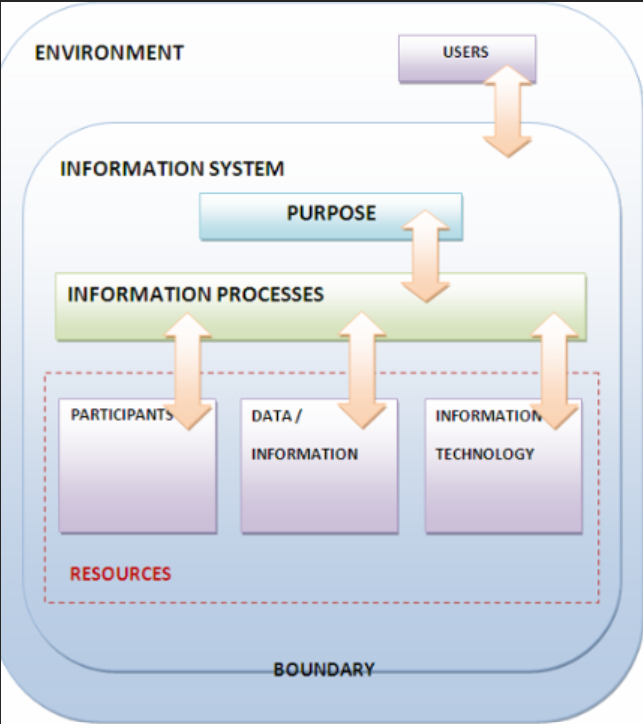
All systems share characteristics that make it easier to comprehend how they work, what is required for them to function, and how information is created from data.
These features include:
- The Environment
- The Boundary
- The Purpose
- Information Processes
- User and participants
- Information Technology
- Resources






Digitalising of data refers to the process through which analogue data is transformed into digital data for use by information systems. For instance, scanning a paper form to create an online form or scanning a document and extracting the text.
created with
Website Builder Software .